Analysis of nucleic acid double helix geometry
| Title | | T DOMAIN FROM XENOPUS LAEVIS BOUND TO DNA |
| PDB code | | 1XBR (PDB summary) |
| NDB code | | PDT045 (NDB atlas) |
| Duplex length | | 24 base pairs |
| Protein | | Brachyury (T protein), Transcription factor, DNA binding domain: T domain |
Only the nucleic acid double helix part of the structure is analysed here. Small ligands, proteins, and overhanging ends are not taken into account. Information on the complete structure is available at the Image Library Entry page and at the Sequence, Chains, Units page.
| Strand 1 | 5' | A501 | A502 | T503 | T504 | T505 | C506 | A507 | C508 | A509 | C510 | C511 | T512 | A513 | G514 | G515 | T516 | G517 | T518 | G519 | A520 | A521 | A522 | T523 | T524 | 3' |
| Strand 2 | 3' | T524 | T523 | A522 | A521 | A520 | G519 | T518 | G517 | T516 | G515 | G514 | A513 | T512 | C511 | C510 | A509 | C508 | A507 | C506 | T505 | T504 | T503 | A502 | A501 | 5' |
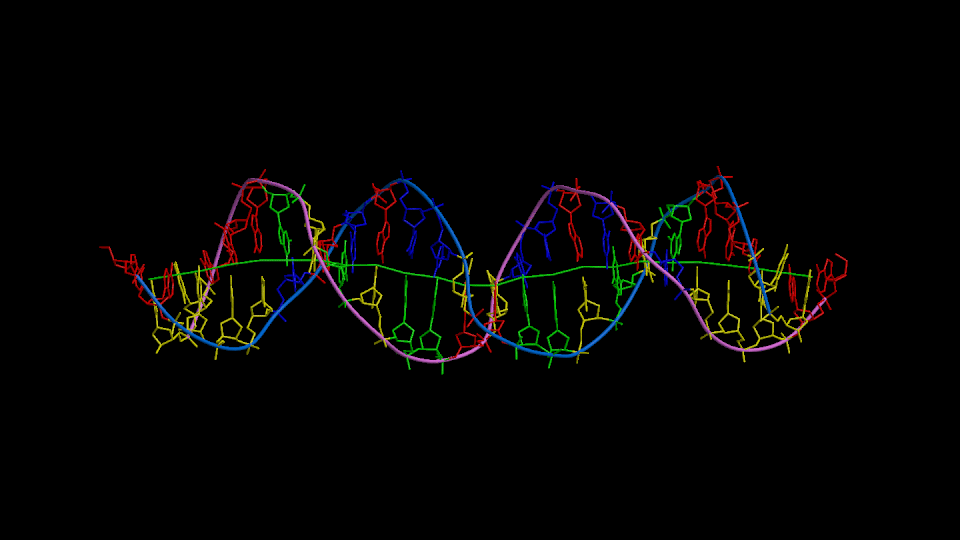
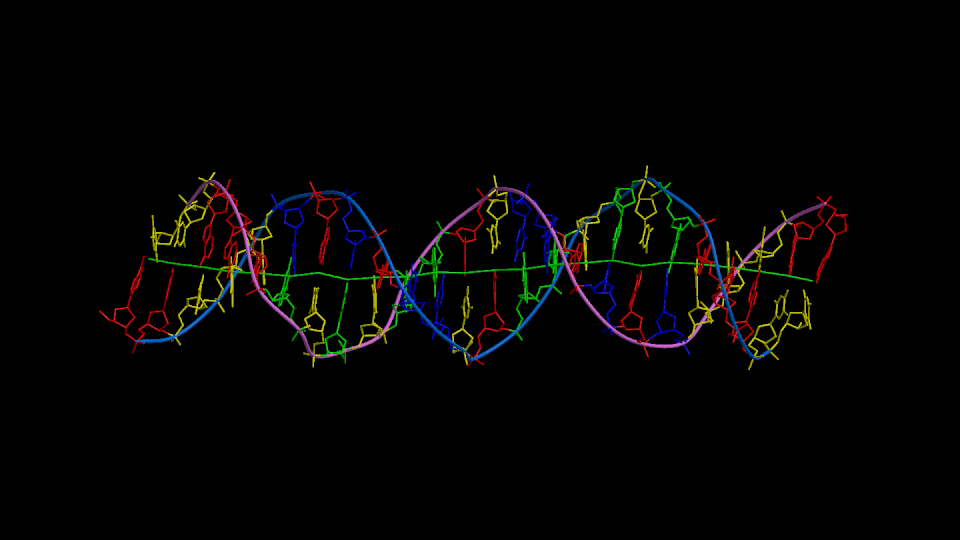
Figure 1
Three orthogonal views of the double helix (Help).
Residues are colored according to the nucleotide type (Help: Color codes).
The curvilinear helical axis (green) was calculated with
CURVES. The
double helix is oriented with respect to the principle axis of inertia
of the curvilinear helical axis (see Help for further explanations).
This drawing reveals immediately if there is any bending of the helical axis.
Analysis of helical axis bending
Inter base pair parameters
The six inter base pair parameters (rise, shift,
slide, twist, roll, tilt) describe the
translational and rotational displacement between neighbouring base
pairs. See Help for further explanations.
Plot of inter base pair parameters with respect to global and local helical axes: PDF, GIF
(Global parameters from CURVES, local parameters from CURVES and FREEHELIX)
Table 1.
Inter base pair parameters with respect to the global helical axis, calculated with CURVES.
|
| Strand 1 | Strand 2 | riseg | shiftg | slideg | twistg | rollg | tiltg |
| | | / Å | / Å | / Å | | | |
|
| A501 | T524 | | | | | | |
| | | 2.9 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 40° | 1° | -4° |
| A502 | T523 | | | | | | |
| | | 3.4 | -0.0 | -0.3 | 32° | 1° | 2° |
| T503 | A522 | | | | | | |
| | | 3.1 | 0.4 | -0.1 | 36° | -2° | 3° |
| T504 | A521 | | | | | | |
| | | 3.4 | -0.2 | -0.3 | 36° | -2° | -6° |
| T505 | A520 | | | | | | |
| | | 3.3 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 37° | -3° | 5° |
| C506 | G519 | | | | | | |
| | | 3.1 | -0.8 | 1.0 | 34° | 2° | -3° |
| A507 | T518 | | | | | | |
| | | 3.4 | 0.4 | -1.2 | 29° | -2° | -1° |
| C508 | G517 | | | | | | |
| | | 3.2 | -0.3 | 1.1 | 38° | 2° | -3° |
| A509 | T516 | | | | | | |
| | | 3.3 | 0.0 | -0.9 | 31° | 6° | -3° |
| C510 | G515 | | | | | | |
| | | 3.7 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 38° | 1° | -3° |
| C511 | G514 | | | | | | |
| | | 3.1 | -1.1 | -0.1 | 27° | 6° | -1° |
| T512 | A513 | | | | | | |
| | | 3.5 | -0.0 | -0.2 | 30° | 15° | 1° |
| A513 | T512 | | | | | | |
| | | 3.0 | 1.2 | 0.1 | 26° | 7° | -2° |
| G514 | C511 | | | | | | |
| | | 3.6 | -0.7 | 0.1 | 43° | -1° | 1° |
| G515 | C510 | | | | | | |
| | | 3.5 | 0.1 | -0.9 | 32° | 5° | 5° |
| T516 | A509 | | | | | | |
| | | 3.2 | 0.1 | 1.1 | 36° | 2° | 3° |
| G517 | C508 | | | | | | |
| | | 3.3 | -0.3 | -1.1 | 31° | -2° | 3° |
| T518 | A507 | | | | | | |
| | | 3.1 | 0.8 | 1.1 | 30° | 3° | -1° |
| G519 | C506 | | | | | | |
| | | 3.2 | -0.1 | 0.3 | 37° | -3° | -2° |
| A520 | T505 | | | | | | |
| | | 3.6 | 0.0 | -0.4 | 35° | 1° | -1° |
| A521 | T504 | | | | | | |
| | | 3.2 | -0.1 | -0.1 | 37° | -3° | -1° |
| A522 | T503 | | | | | | |
| | | 3.3 | -0.1 | -0.2 | 34° | -1° | 2° |
| T523 | A502 | | | | | | |
| | | 2.9 | -0.0 | 0.3 | 38° | 0° | -0° |
| T524 | A501 | | | | | | |
|
Backbone parameters
Table 2. Selected torsional angles and sugar pucker phase angles describing the conformation of the sugar phosphate backbone. (See Help for further explanations.)
|
| gamma | epsilon-zeta | pucker | chi | Strand 1 | Strand 2 | chi | pucker | epsilon-zeta | gamma |
|
| | | C2'-endo | -121° | A501 | T524 | -87° | C3'-exo | | |
| 46° | -75° (BI) | | | | | | | -40° (BI) | 42° |
| | | C2'-endo | -101° | A502 | T523 | -111° | C2'-endo | | |
| 45° | -86° (BI) | | | | | | | -73° (BI) | 44° |
| | | C2'-endo | -107° | T503 | A522 | -105° | C2'-endo | | |
| 51° | -64° (BI) | | | | | | | -70° (BI) | 42° |
| | | C2'-endo | -108° | T504 | A521 | -93° | C2'-endo | | |
| 49° | -63° (BI) | | | | | | | -91° (BI) | 45° |
| | | C2'-endo | -118° | T505 | A520 | -115° | C2'-endo | | |
| 5° | -29° (BI) | | | | | | | 74° (BII) | 49° |
| | | C2'-endo | -93° | C506 | G519 | -83° | C2'-endo | | |
| 46° | 23° (BII) | | | | | | | -49° (BI) | 46° |
| | | C2'-endo | -98° | A507 | T518 | -124° | C2'-endo | | |
| 18° | -68° (BI) | | | | | | | -75° (BI) | 59° |
| | | C2'-endo | -107° | C508 | G517 | -118° | C2'-endo | | |
| 47° | 7° (BI) | | | | | | | -35° (BI) | -83° |
| | | C2'-endo | -99° | A509 | T516 | -125° | C2'-endo | | |
| 21° | -75° (BI) | | | | | | | -41° (BI) | 44° |
| | | C1'-exo | -102° | C510 | G515 | -122° | C2'-endo | | |
| -121° | -23° (BI) | | | | | | | 26° (BII) | 42° |
| | | C2'-endo | -150° | C511 | G514 | -104° | C2'-endo | | |
| 56° | -74° (BI) | | | | | | | -63° (BI) | 23° |
| | | C2'-endo | -117° | T512 | A513 | -103° | C2'-endo | | |
| -53° | -57° (BI) | | | | | | | -75° (BI) | 55° |
| | | C2'-endo | -100° | A513 | T512 | -114° | C2'-endo | | |
| 45° | -76° (BI) | | | | | | | -73° (BI) | -107° |
| | | C2'-endo | -101° | G514 | C511 | -145° | C4'-endo | | |
| 49° | 23° (BII) | | | | | | | -21° (BI) | 28° |
| | | C2'-endo | -119° | G515 | C510 | -109° | C1'-exo | | |
| -89° | -48° (BI) | | | | | | | -82° (BI) | 55° |
| | | C3'-exo | -130° | T516 | A509 | -104° | C2'-endo | | |
| 62° | -46° (BI) | | | | | | | -32° (BI) | -9° |
| | | C2'-endo | -116° | G517 | C508 | -105° | C1'-exo | | |
| -59° | -53° (BI) | | | | | | | -56° (BI) | 48° |
| | | C3'-exo | -115° | T518 | A507 | -95° | C2'-endo | | |
| 46° | -66° (BI) | | | | | | | 15° (BI) | 2° |
| | | C2'-endo | -90° | G519 | C506 | -91° | C2'-endo | | |
| 48° | 42° (BII) | | | | | | | -19° (BI) | 55° |
| | | C2'-endo | -113° | A520 | T505 | -114° | C2'-endo | | |
| 40° | -70° (BI) | | | | | | | -77° (BI) | 53° |
| | | C2'-endo | -109° | A521 | T504 | -109° | C2'-endo | | |
| 45° | -71° (BI) | | | | | | | -76° (BI) | 43° |
| | | C2'-endo | -109° | A522 | T503 | -109° | C1'-exo | | |
| 41° | -71° (BI) | | | | | | | -75° (BI) | 46° |
| | | C2'-endo | -107° | T523 | A502 | -89° | C2'-endo | | |
| -62° | -34° (BI) | | | | | | | -91° (BI) | 39° |
| | | C3'-exo | -85° | T524 | A501 | -141° | C2'-endo | | |
|
Groove width
| Plot of minor groove width: | PDF, GIF |
| Plot of major groove width: | PDF, GIF |
| (See Help for further explanations.)
|
Further information
Full output from CURVES (helical parameters with respect to global and local axes)
Full output from FREEHELIX (helical parameters with respect to local axis, angles between normal vectors)
Chirality of ribose and phosphate atoms
Check the naming of phosphate and ribose substituents. Recommended for phosphate oxygens and for ribose hydrogens in NMR structures.