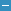
Asymmetric/Biological Unit(show GO term definitions)
Chain A ( ILF2_MOUSE | Q9CXY6)
| molecular function |
|---|
| | GO:0005524 | | ATP binding | | Interacting selectively and non-covalently with ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| | GO:0003677 | | DNA binding | | Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively and non-covalently with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). |
| | GO:0003723 | | RNA binding | | Interacting selectively and non-covalently with an RNA molecule or a portion thereof. |
| | GO:0003725 | | double-stranded RNA binding | | Interacting selectively and non-covalently with double-stranded RNA. |
| | GO:0016740 | | transferase activity | | Catalysis of the transfer of a group, e.g. a methyl group, glycosyl group, acyl group, phosphorus-containing, or other groups, from one compound (generally regarded as the donor) to another compound (generally regarded as the acceptor). Transferase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 2. |
| biological process |
|---|
| | GO:0006955 | | immune response | | Any immune system process that functions in the calibrated response of an organism to a potential internal or invasive threat. |
| | GO:0045893 | | positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| | GO:0006355 | | regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| | GO:0006351 | | transcription, DNA-templated | | The cellular synthesis of RNA on a template of DNA. |
| cellular component |
|---|
| | GO:0005737 | | cytoplasm | | All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| | GO:0030529 | | intracellular ribonucleoprotein complex | | An intracellular macromolecular complex containing both protein and RNA molecules. |
| | GO:0016020 | | membrane | | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| | GO:0005730 | | nucleolus | | A small, dense body one or more of which are present in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is rich in RNA and protein, is not bounded by a limiting membrane, and is not seen during mitosis. Its prime function is the transcription of the nucleolar DNA into 45S ribosomal-precursor RNA, the processing of this RNA into 5.8S, 18S, and 28S components of ribosomal RNA, and the association of these components with 5S RNA and proteins synthesized outside the nucleolus. This association results in the formation of ribonucleoprotein precursors; these pass into the cytoplasm and mature into the 40S and 60S subunits of the ribosome. |
| | GO:0005654 | | nucleoplasm | | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| | GO:0005634 | | nucleus | | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
Chain B ( ILF3_MOUSE | Q9Z1X4)
| molecular function |
|---|
| | GO:0003677 | | DNA binding | | Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively and non-covalently with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). |
| | GO:0003723 | | RNA binding | | Interacting selectively and non-covalently with an RNA molecule or a portion thereof. |
| | GO:0003725 | | double-stranded RNA binding | | Interacting selectively and non-covalently with double-stranded RNA. |
| biological process |
|---|
| | GO:0051607 | | defense response to virus | | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a virus that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| | GO:0045892 | | negative regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| | GO:0017148 | | negative regulation of translation | | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of proteins by the translation of mRNA or circRNA. |
| | GO:0045071 | | negative regulation of viral genome replication | | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of viral genome replication. |
| | GO:0045893 | | positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| | GO:0006479 | | protein methylation | | The addition of a methyl group to a protein amino acid. A methyl group is derived from methane by the removal of a hydrogen atom. |
| | GO:0006468 | | protein phosphorylation | | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| | GO:0006355 | | regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| | GO:0006351 | | transcription, DNA-templated | | The cellular synthesis of RNA on a template of DNA. |
| cellular component |
|---|
| | GO:0005737 | | cytoplasm | | All of the contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| | GO:0030529 | | intracellular ribonucleoprotein complex | | An intracellular macromolecular complex containing both protein and RNA molecules. |
| | GO:0016020 | | membrane | | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| | GO:0005739 | | mitochondrion | | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| | GO:0005730 | | nucleolus | | A small, dense body one or more of which are present in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is rich in RNA and protein, is not bounded by a limiting membrane, and is not seen during mitosis. Its prime function is the transcription of the nucleolar DNA into 45S ribosomal-precursor RNA, the processing of this RNA into 5.8S, 18S, and 28S components of ribosomal RNA, and the association of these components with 5S RNA and proteins synthesized outside the nucleolus. This association results in the formation of ribonucleoprotein precursors; these pass into the cytoplasm and mature into the 40S and 60S subunits of the ribosome. |
| | GO:0005654 | | nucleoplasm | | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| | GO:0005634 | | nucleus | | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
|



 Description
Description
 Compounds
Compounds
 Chains, Units
Chains, Units
 Ligands, Modified Residues, Ions (2, 2)
Ligands, Modified Residues, Ions (2, 2)
 Sites (2, 2)
Sites (2, 2)
 SS Bonds (0, 0)
SS Bonds (0, 0)
 Cis Peptide Bonds (2, 2)
Cis Peptide Bonds (2, 2)
 SAPs(SNPs)/Variants (0, 0)
SAPs(SNPs)/Variants (0, 0)
 PROSITE Motifs (1, 1)
PROSITE Motifs (1, 1)
 Exons (0, 0)
Exons (0, 0)
 Sequences/Alignments
Sequences/Alignments
 SCOP Domains (0, 0)
SCOP Domains (0, 0)
 CATH Domains (0, 0)
CATH Domains (0, 0)
 Pfam Domains (0, 0)
Pfam Domains (0, 0)
 Gene Ontology (22, 34)
Gene Ontology (22, 34)
 Interactive Views
Interactive Views
 Still Images
Still Images
 Databases
Databases
 Analysis Tools
Analysis Tools
 Entries Sharing at Least One Protein Chain (UniProt ID)
Entries Sharing at Least One Protein Chain (UniProt ID)
 Related Entries Specified in the PDB File
Related Entries Specified in the PDB File