

Nucleic Acid Nomenclature and Structure
compiled by
Christoph Schneider, -- Biocomputing -- Group at IMB Jena
loading this page may take a while
structures of the five major purine (R) and
pyrimidine (Y) bases of nucleic acids in their dominant tautomeric
forms and with the IUPAC numbering system
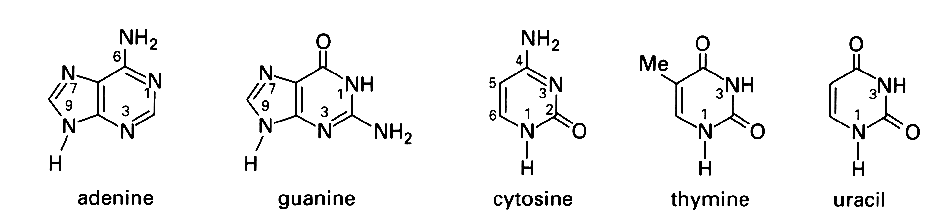
Source: Blackburn and Gait, Nucleic acids in chemistry and biology,
Oxford University Press New York 1996.
atomic numbering scheme and definition of
torsion angles for a polyribonucleotide chain
For other information on backbone torsional angles click here.

Source: Saenger,W., Principles of Nucleic Acid Structure, Springer
Verlag New York 1984.
pseudorotation
cycle of the furanose ring in nucleosides.
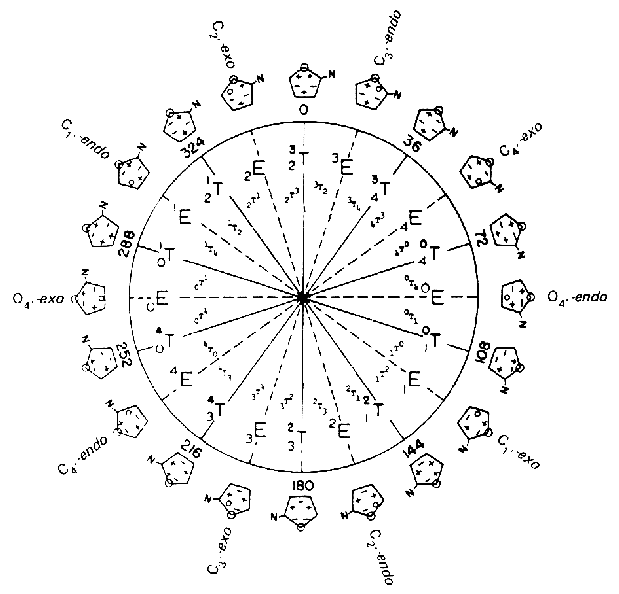
Source: Saenger,W., Principles of
Nucleic Acid Structure, Springer Verlag New York 1984.
ideal B-DNA is C2'-endo (South), ideal A-RNA is C3'-endo (North) 
anti and syn conformational ranges
for glycosydic bonds in pyrimidine (left) and purine (right) nucleosides

Source: Blackburn and Gait,
Nucleic acids in chemistry and biology, Oxford University Press New
York 1996.
(More detailed information on base pairs can be found in the Base Pair Directory).
The 28 possible base pairs that
involve at least two hydrogen bonds as compiled by I. Tinoco Jr.
the seven possible
pyrimidine-pyrimidine base pairs

Source: Ignacio Tinoco, Jr. in
Gesteland, R. F. and Atkins, J. F. (1993) THE RNA WORLD. Cold Spring
Harbor Laboratory Press.
proposed hydrogen-bonding schemes for base triples. nucleotide triples occur when single-stranded nucleotides form hydrogen bonds with nucleotides that are already base paired (see also pseudoknots).
Proposed
hydrogen-bonding schemes for base triples.

Source: Chastain, M. and Tinoco
Jr., I., (1991) Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 41,
131-177.

Source: Blackburn and Gait,
Nucleic acids in chemistry and biology, Oxford University Press New
York 1996.
R.E. Dickerson et al. (1989) Nucleic
Acids Res. 17, 1797-1803.
secondary
structure of RNA consists of duplex and loop regions that can be
divided into six different types: duplexes, single-stranded regions,
hairpins, internal loops or bubbles, bulge loops or bulges and
junctions.

Source: Chastain, M. and Tinoco
Jr., I., (1991) Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 41,
131-177.
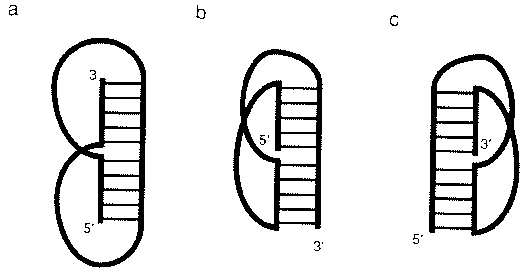
Source: Chastain, M. and Tinoco
Jr., I., (1991) Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 41,
131-177.
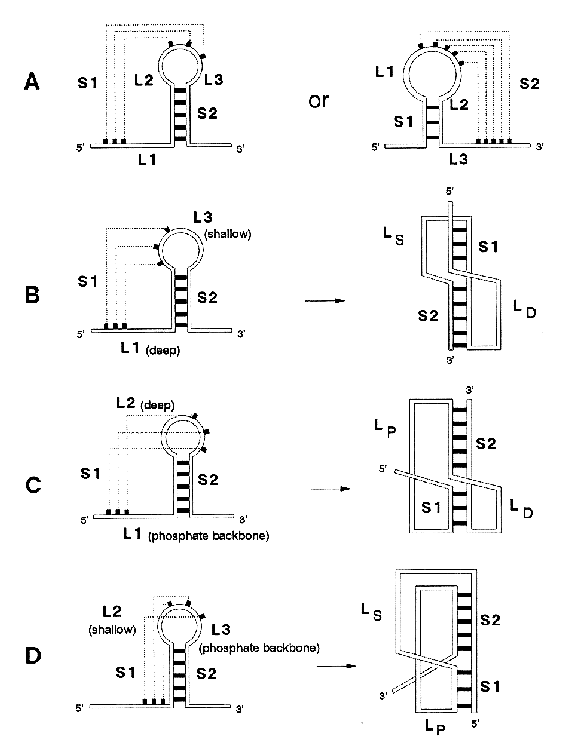
Source: Cornelis W. A. Pleij in
Gesteland, R. F. and Atkins, J. F. (1993) THE RNA WORLD. Cold Spring
Harbor Laboratory Press.